Molecular hydrogen as a potential adjunctive treatment for cancer

In recent years, has been growing interest in the potential of H2 therapy for the treatment of cancer. H2 has a number of properties that make it a promising cancer treatment:
Click here for H2 & Cancer research papers
Antioxidant
It is a powerful antioxidant, meaning that it can help to protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage DNA and other cellular structures. They are thought to play a role in the development of cancer.
Hydrogen can help to reduce oxidative stress, which can damage cells and contribute to the development of cancer.
Anti-inflammatory
H2 also has anti-inflammatory effects. Inflammation is a process that can contribute to the growth and spread of cancer. H2 can help to reduce inflammation by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Hydrogen's anti-inflammatory effects may help to reduce the growth and spread of cancer.
Anti-apototic
In addition, H2 has been shown to have anti-apoptotic effects. Apoptosis is a natural process of cell death that is essential for maintaining the health of the body. Cancer cells often evade apoptosis, which allows them to survive and multiply. H2 can help to induce apoptosis in cancer cells, which can lead to their death.
Reduce Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy side effects
Evidence from research studies indicates that hydrogen therapy can help to protect cells from damage caused by chemotherapy and radiation therapy.

Two main mechanisms of hydrogen (H2) cancer control. Note: PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1.
A narrative review of hydrogen oncology: from real world survey to real world evidence
Scientific Studies
There have been a number of studies that have investigated the potential of H2 therapy for the treatment of cancer. These studies have shown that H2 can be effective in inhibiting the growth of cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. In some cases, H2 has been shown to be as effective as traditional cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
However, more research is needed to fully understand the potential of H2 therapy for the treatment of cancer. Currently, H2 therapy is not a standard treatment for cancer. However, it is a promising area of research and there is potential for H2 to be used as an adjunct therapy or as a way to reduce the side effects of traditional cancer treatments.
Below is the summary of a scientific paper in 2019
Li S, Liao R, Sheng X, Luo X, Zhang X, Wen X, Zhou J, Peng K. Hydrogen Gas in Cancer Treatment. Front Oncol. 2019 Aug 6;9:696.Recently, hydrogen gas (H2) has gained attention for its potential in cancer treatment. Studies have shown that hydrogen gas can reduce the side effects of chemotherapy, inhibit the growth of cancer cells, and even suppress tumor growth in animal models. The mechanisms of action involve the regulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), inflammation, and apoptosis. Hydrogen gas selectively scavenges harmful ROS, induces antioxidant enzymes to eliminate ROS, and modulates inflammatory cytokines. It can also regulate apoptosis by impacting the expression of apoptosis-related enzymes. Furthermore, hydrogen gas has been found to relieve the adverse effects of chemotherapy and radiotherapy, such as oxidative stress and inflammation. It has shown protective effects on the heart, liver, and kidneys in animal studies.
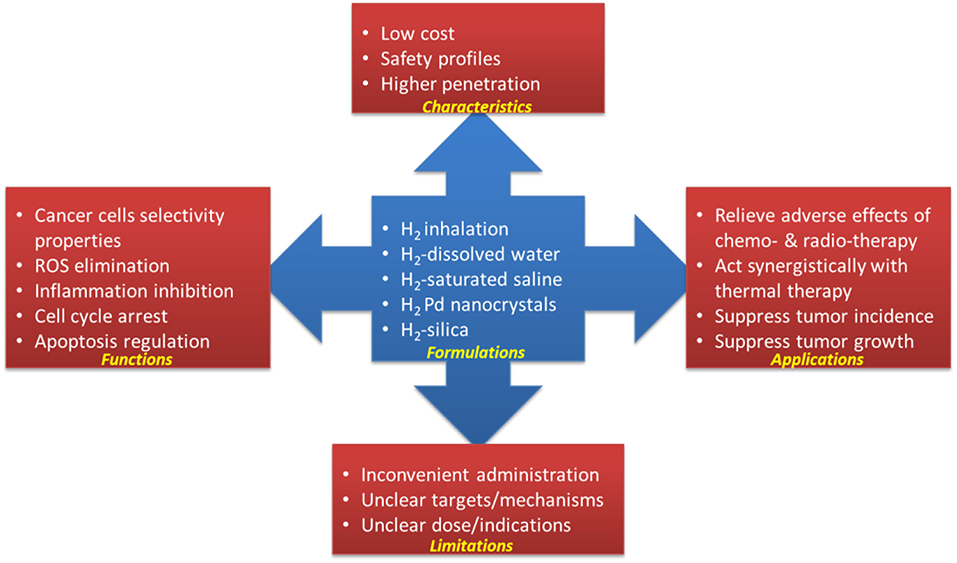
However, it is important to note that more research is needed to fully understand the potential of molecular hydrogen for cancer treatment. Currently, it is not a standard treatment for cancer. However, it is a promising area of research and there is potential for molecular hydrogen to be used as an adjunct therapy or as a way to reduce the side effects of traditional cancer treatments.
Click here to buy H Fizz H2 products to support cancer therapy & recovery
To further explore, below are scientific studies on molecular hydrogen and cancer for your reference:
Lian N, Shen M, Zhang K, Pan J, Jiang Y, Yu Y, Yu Y. Drinking Hydrogen-Rich Water Alleviates Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain Through the Regulation of Gut Microbiota. J Pain Res. 2021;14:681-691https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S288289
Li S, Liao R, Sheng X, Luo X, Zhang X, Wen X, Zhou J, Peng K. Hydrogen Gas in Cancer Treatment. Front Oncol. 2019 Aug 6;9:696. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00696. PMID: 31448225; PMCID: PMC6691140.
Zhang X, Tao G, Zhao Y, et al. Molecular Hydrogen Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Growth via the AKT/SCD1 Signaling Pathway. BioMed Research International. 2022;2022:e8024452. doi:https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8024452
Xu KC, Chen JB, Kong XF, et al. “Real world survey” of hydrogen-controlled cancer: a follow-up report of 82 advanced cancer patients. Medical Gas Research. 2019;9(3):115. doi:https://doi.org/10.4103/2045-9912.266985
Zhu B, Cui H, Xu W. Hydrogen inhibits the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells by modulating lncRNA MALAT1/miR-124-3p/EZH2 axis. Cancer Cell International. 2021;21(1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01743-5
Zhang X, Tao G, Zhao Y, et al. Molecular Hydrogen Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Growth via the AKT/SCD1 Signaling Pathway. Gagat M, ed. BioMed Research International. 2022;2022:1-11. doi:https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8024452
ND CD. Hydrogen as a Tool in the Fight to Reduce Cancer Treatment Side Effects. Today’s Practitioner. Published April 22, 2020. Accessed November 16, 2022. https://todayspractitioner.com/hydrogen/molecular-hydrogen-as-a-tool-in-the-fight-to-reduce-cancer-treatment-side-effects/#.Y3Rr3HYzaUk
Cole AR, Sperotto F, DiNardo JA, et al. Safety of Prolonged Inhalation of Hydrogen Gas in Air in Healthy Adults. Critical Care Explorations. 2021;3(10):e543. doi:https://doi.org/10.1097/CCE.000000000000054
Chen J, Kong X, Mu F, Lu T, Du D, Xu K. Hydrogen-oxygen therapy can alleviate radiotherapy-induced hearing loss in patients with nasopharyngeal cancer. Annals of Palliative Medicine. 2019;8(5):746-751. doi:https://doi.org/10.21037/apm.2019.11.18
Hirano SI, Aoki Y, Li XK, Ichimaru N, Takahara S, Takefuji Y. Protective effects of hydrogen gas inhalation on radiation-induced bone marrow damage in cancer patients: a retrospective observational study. Medical Gas Research. 2021;11(3):104-109. doi:https://doi.org/10.4103/2045-9912.314329
Chen JB, Lu YY, Xu KC. A narrative review of hydrogen oncology: from real world survey to real world evidence. Medical Gas Research. 2020;10(3):0. doi:https://doi.org/10.4103/2045-9912.296044
Mohd Noor MNZ, Alauddin AS, Wong YH, et al. A Systematic Review of Molecular Hydrogen Therapy in Cancer Management. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention. 2023;24(1):37-47. doi:https://doi.org/10.31557/apjcp.2023.24.1.37
Yang Y, Zhu Y, Xi X. Anti‑inflammatory and antitumor action of hydrogen via reactive oxygen species (Review). Oncology Letters. Published online June 26, 2018. doi:https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.9023
Yang Y, Zhu Y, Xi X. Anti‑inflammatory and antitumor action of hydrogen via reactive oxygen species (Review). Oncology Letters. Published online June 26, 2018. doi:https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.9023

